在jdk1.5中引入了注解的概念,注解是Java提供的一种对类信息(包括:类、属性与方法)进行扩展的一种行为。Annatation(注解)是一个接口,程序可以通过反射来获取指定程序中元素的 Annotation 对象,然后通过该 Annotation 对象来获取注解中的元数据信息。通过使用注解,可以将元数据保存在 Java 源代码中。并拥有如下优势:
- 简单易读的代码,
- 编译器类型检查,
- 使用 annotation API 为自己的注解构造处理工具。
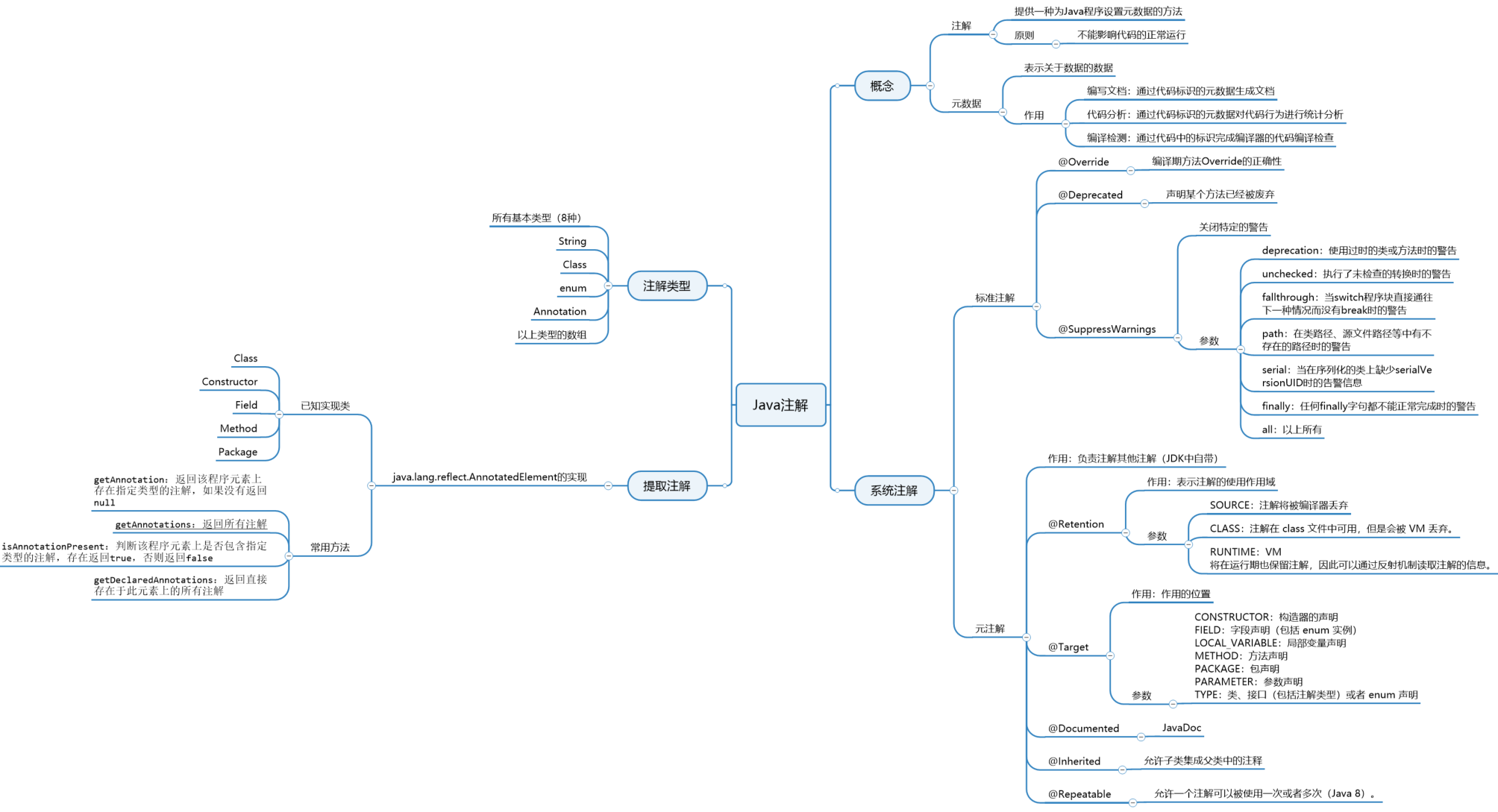
JDK中目前引入的注解:
- @Override:表示当前的方法定义将覆盖基类的方法。如果你不小心拼写错误,或者方法签名被错误拼写的时候,编译器就会发出错误提示。
- @Deprecated:如果使用该注解的元素被调用,编译器就会发出警告信息。
- @SuppressWarnings:关闭不当的编译器警告信息。
- @SafeVarargs:在 Java 7 中加入用于禁止对具有泛型varargs参数的方法或构造函数的调用方发出警告。
- @FunctionalInterface:Java 8 中加入用于表示类型声明为函数式接口
定义
jdk中目前定义了5中标准的meta-annotation 类型,它们被用来提供对其它 annotation 类型作说明。
| 注解 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| @Target | 表示注解可以用于哪些地方。可能的 ElementType 参数包括: CONSTRUCTOR:构造器的声明 FIELD:字段声明(包括 enum 实例) LOCAL_VARIABLE:局部变量声明 METHOD:方法声明 PACKAGE:包声明 PARAMETER:参数声明 TYPE:类、接口(包括注解类型)或者 enum 声明 |
| @Retention | 表示注解信息保存的时长。可选的 RetentionPolicy 参数包括: SOURCE:注解将被编译器丢弃 CLASS:注解在 class 文件中可用,但是会被 VM 丢弃。 RUNTIME:VM 将在运行期也保留注解,因此可以通过反射机制读取注解的信息。 |
| @Documented | 将此注解保存在 Javadoc 中 |
| @Inherited | 允许子类继承父类的注解 |
| @Repeatable | 允许一个注解可以被使用一次或者多次(Java 8)。 |
@Target修饰的对象范围
@Target说明了Annotation所修饰的对象范围: Annotation可被用于 packages、types(类、接口、枚举、Annotation 类型)、类型成员(方法、构造方法、成员变量、枚举值)、方法参数和本地变量(如循环变量、catch 参数)。在 Annotation 类型的声明中使用了 target 可更加明晰其修饰的目标。
1 |
|
具体的作用范围:
1 | public enum ElementType { |
@Retention定义被保留的时间长短
@Retention 定义了该 Annotation 被保留的时间长短:表示需要在什么级别保存注解信息,用于描述注解的生命周期(即:被描述的注解在什么范围内有效),取值(RetentionPoicy)由:
- SOURCE:在源文件中有效(即源文件保留)
- CLASS:在 class 文件中有效(即 class 保留)
- RUNTIME:在运行时有效(即运行时保留)
1 |
|
具体作用范围:
1 | public enum RetentionPolicy { |
@Documented描述-javadoc
@Documented 用于描述其它类型的 annotation 应该被作为被标注的程序成员的公共 API,因此可以被例如 javadoc 此类的工具文档化。
1 |
|
@Inherited阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的
@Inherited 元注解是一个标记注解,**@Inherited** 阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的。如果一个使用了**@Inherited** 修饰的 annotation 类型被用于一个 class,则这个 annotation 将被用于该 class 的子类。
1 |
|
@Repeatable
1 |
|
示例
通过注解实现一种日志记录的方式。
LogAnnotation定义
1 |
|
注解使用
1 | public class Login { |
注解元数据解析
getDeclaredMethods() 和 getAnnotation(),它们都属于 AnnotatedElement 接口(Class,Method 与 Field 类都实现了该接口)。getAnnotation() 方法返回指定类型的注解对象。
1 | public class AnnotationUtil { |
其他说明
默认值问题
- 元素不能有不确定的值:要么使用默认值要么使用代码中定义的值
- 非基本类型的原始不能定义null,可以使用自定义约束来进行实现
注解不支持继承
应用场景
- 单元测试
- 数据库相关的ORM操作

