概述
API描述
1 | * This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from |
ThreadLocal提供一种线程本地变量。这种变量是一种副本的概念,在多线程环境下访问(get、set)能够保证各个线程间的变量互相隔离。ThreadLocal通常定义为了private static,用来关联线程和线程上下文(比如userId或事物ID)。ThreadLocal 的作用是提供线程内的局部变量,这种变量在线程的生命周期内起作用,减少同一个线程内多个函数或者组件之间一些公共变量的传递的复杂度。
使用说明
- 让某个需要用到的对象实现线程之间的隔离(每个线程都有自己独立的对象)
- 可以在任何方法中轻松的获取到该对象
- 根据共享对象生成的时机选择使用initialValue方法还是set方法
- 对象初始化的时机由我们控制的时候使用initialValue 方式
- 如果对象生成的时机不由我们控制的时候使用 set 方式
优点
- 达到线程安全的目的
- 不需要加锁,执行效率高
- 更加节省内存,节省开销
- 免去传参的繁琐,降低代码耦合度
ThreadLocal与锁的区别
- lock 的资源是多个线程共享的,所以访问的时候需要加锁。
- ThreadLocal 是每个线程都有一个副本,是不需要加锁的。
- lock 是通过时间换空间的做法。
- ThreadLocal 是典型的通过空间换时间的做法。
结构解析
JDK早期设计
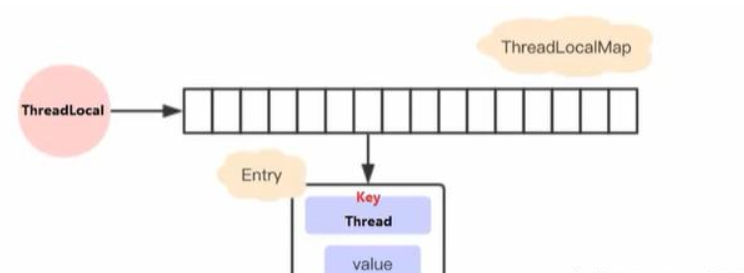
在早期的设计中每个 ThreadLocal 创建一个 ThreadLocalMap,然后用线程作为 Map 的 key,要存储的局部变量作为 Map 的 value,这样达到线程隔离的目的。由于该线程绑定的变量不能被自动的回收,因为变量存储在 ThreadLocal 里,必须显式的去回收。(容易出现内存泄露)
JDK1.8设计
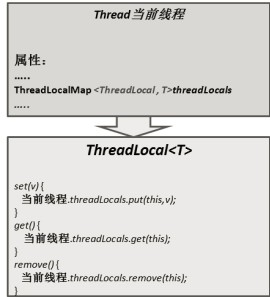
在Thread类中维护了ThreadLocalMap;这个变量用于存储ThreadLocal,因为在同一个线程当中可以有多个ThreadLocal,并且多次调用get()所以需要在内部维护一个ThreadLocalMap用来存储多个ThreadLocal。Thread中的代码如下:
1 | /* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained |
如下图所示:
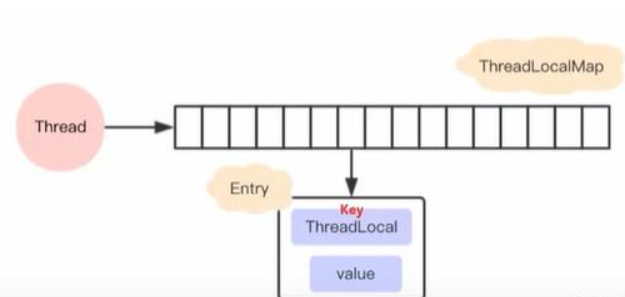
通过代码分析得出以下结论:
- ① 每个
Thread内部都有一个ThreadLocalMapThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;达到线程隔离 - ②
ThreadLocalMap里面存储ThreadLocal对象(key) 和 线程的变量副本(value)t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);;使用静态并ThreadLocal作为key,将不同对象的引用保存到不同线程的ThreadLocalMap中。 - ③
Thread内部的ThreadLocalMap是由ThreadLocal维护的,由ThreadLocal负责向 ThreadLocalMap 设置和获取变量值 - ④ 对于不同的线程,每次获取副本值时,别的线程并不能获取当前线程的副本值,形成副本的隔离,互不干扰
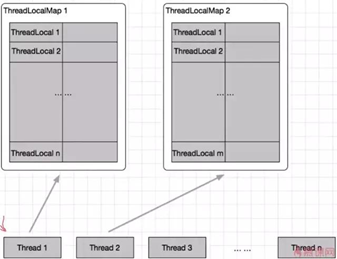
如下图所示:
好处:
- ① 每个 ThreadLocalMap 存储的 Entry 数量变少
- ② 当 Thread 销毁时,ThreadLocalMap 也随之销毁,减少内存的使用
源码解析
get
获取当前线程中绑定的局部两类。
1 | /** |
set
使用线程本地变量的方式存储数据,绑定到当前线程中。
1 | /** |
reomove
清空数据,防止内存泄露
1 | /** |
initialValue
该方法用于设置初始值,并且在调用get()方法时才会被触发,所以是懒加载。但是如果在get()之前进行了set()操作,这样就不会调用initialValue()。通常每个线程只能调用一次本方法,但是调用了remove()后就能再次调用.
1 | /** |
ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap类图
ThreadLocalMap源码
1 | /** |
通过源码分析ThreadLocalMap与HashMap的结构类似。
ThreadLocalMap保存数据
1 | /** |
通过源码分析如下:
每个
ThreadLocal对象都有一个hash值threadLocalHashCode,每初始化一个ThreadLocal对象,hash值就增加一个固定的大小 0x61c88647 。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18/**
* ThreadLocals rely on per-thread linear-probe hash maps attached
* to each thread (Thread.threadLocals and
* inheritableThreadLocals). The ThreadLocal objects act as keys,
* searched via threadLocalHashCode. This is a custom hash code
* (useful only within ThreadLocalMaps) that eliminates collisions
* in the common case where consecutively constructed ThreadLocals
* are used by the same threads, while remaining well-behaved in
* less common cases.
*/
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
/**
* Returns the next hash code.
*/
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}在set数据时首先根据
threadLocalHashCode对key进行hash,如果当前位置没数据数据则初始化一个Entry放到该位置上。如果有数据则继续判断当前位置的key是否与当前设置的key相同,如果是则替换当前Entry中的value
如果key不同则for循环继续查找。
ThreadLocalMap与HashMap的区别
主要体现在hash冲突解决上。
- HashMap 的数据结构是数组+链表
- ThreadLocalMap的数据结构仅仅是数组
- HashMap 是通过链地址法解决hash 冲突的问题
- ThreadLocalMap 是通过开放地址法来解决hash 冲突的问题
- HashMap 里面的Entry 内部类的引用都是强引用
- ThreadLocalMap里面的Entry 内部类中的key 是弱引用,value 是强引用
问题
内存泄露
某个对象不会再被使用,但是该对象的内存却无法被收回。
Java引用的说明(后续会在JVM垃圾回收中详细说明)
Java中存在四种引用类型:强、弱、软、虚
- 强引用:最常见的是使用new创建的对象,只要存在对象引用,GC就不会回收
- 软引用:
SoftReference实现,当系统内存不足时才会被回收 - 弱引用:
WeakReference实现,GC 一旦发现弱引用的对象,不管当前内存空间足够与否,都会回收它的内存 - 虚引用:
PhantomReference实现,必须和引用队列联合使用,主要用于跟踪对象被垃圾回收的状态
1 | /** |
原因分析
- 正常情况: 当Thread运行结束后,ThreadLocal中的value会被回收,因为没有任何强引用了
- 非正常情况
当Thread一直在运行始终不结束,强引用就不会被回收,存在以下调用链 Thread–>ThreadLocalMap–>Entry(key为null)–>value因为调用链中的 value 和 Thread 存在强引用,所以value无法被回收,就有可能出现OOM。JDK的设计已经考虑到了这个问题,所以在set()、remove()、resize()方法中会扫描到key为null的Entry,并且把对应的value设置为null,这样value对象就可以被回收。
1 | /** |
但是只有在调用set()、remove()、resize()这些方法时才会进行这些操作,如果没有调用这些方法并且线程不停止,那么调用链就会一直存在,所以可能会发生内存泄漏。
ThreadLocalMap.Entry被定义为弱引用的原因
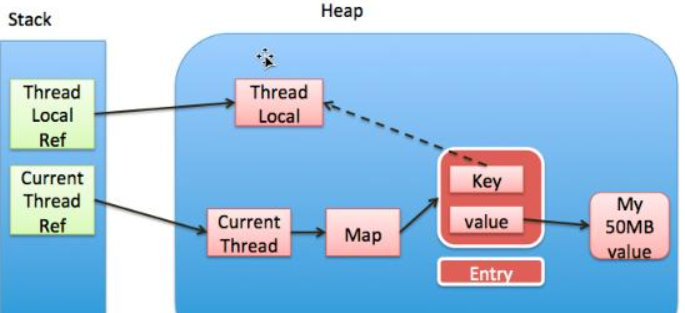
ThreadLocal作为Map中的key,被定义为弱引用,当把ThreadLocal实例设置为null时,gc就可以顺利回收ThreadLocal。但是如果value正常被当前线程使用,只有在当前线程结束之后才能被回收,这也是JDK1.8之后的升级,降低内存泄露的概率。
避免方式
调用remove()方法,就会删除对应的Entry对象,可以避免内存泄漏,所以使用完ThreadLocal后,要调用remove()方法。
空指针问题
调用get方法如果返回值为基本类型,则会出现空指针异常,如果是包装类则不会出现。
共享对象问题
如果在每个线程中ThreadLocal.set()进去的东西本来就是多个线程共享的同一对象,比如static对象,那么多个线程调用ThreadLocal.get()获取的内容还是同一个对象,还是会发生线程安全问题。
可以不使用ThreadLocal就不要强行使用
如果在任务数很少的时候,在局部方法中创建对象就可以解决问题,这样就不需要使用ThreadLocal。
优先使用框架的支持,而不是自己创造
例如在Spring框架中,如果可以使用RequestContextHolder,那么就不需要自己维护ThreadLocal,因为自己可能会忘记调用remove()方法等,造成内存泄漏。
源码参考(RequestContextHolder)
1 | /* |
使用场景
To keep state with a thread (user-id, transaction-id, logging-id)
To cache objects which you need frequently
最常见的 ThreadLocal 使用场景为 用来解决 数据库连接、Session 管理等。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18public class TestThreadLocal {
private static final ThreadLocal<Session> threadSession = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static Session getSession() throws InfrastructureException {
Session s = (Session) threadSession.get();
try {
if (s == null) {
s = getSessionFactory().openSession();
threadSession.set(s);
}
} catch (HibernateException ex) {
throw new InfrastructureException(ex);
}
return s;
}
}其他
如果父子线程共享变量
InheritableThreadLocal
hash冲突解决
链地址法
hash(key)之后的地址i构成一个同义词单链表,并将单链表的头指针存在哈希表的第i个单元中,因而查找、插入和删除主要在同义词链中进行。
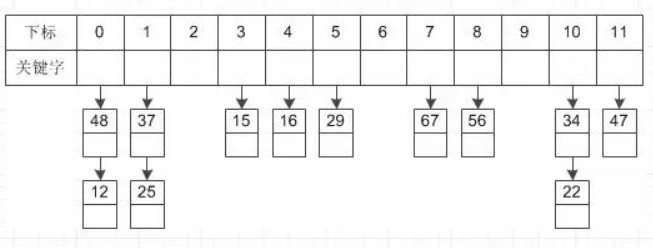
链地址法特点
- 处理冲突简单,且无堆积现象,平均查找长度短。
- 链表中的结点是动态申请的,适合构造表不能确定长度的情况。
- 删除结点的操作易于实现。只要简单地删去链表上相应的结点即可。
- 指针需要额外的空间,故当结点规模较小时,开放定址法较为节省空间。
开放地址法(线性探测法)
hash(key)一旦发生了冲突,就去寻找下一个空的散列地址,只要散列表足够大,空的散列地址总能找到,并将记录存入。
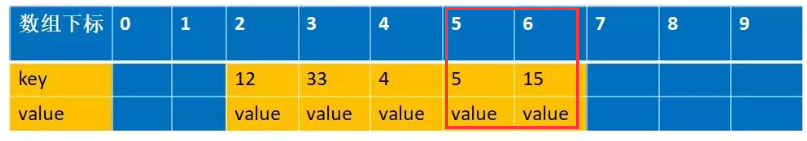
开放地址法特点
- 容易产生堆积问题,不适于大规模的数据存储。
- 散列函数的设计对冲突会有很大的影响,插入时可能会出现多次冲突的现象。
- 删除的元素是多个冲突元素中的一个,需要对后面的元素作处理,实现较复杂。
ThreadLocalMap采用开放地址法原因
- ThreadLocal 中看到一个属性 HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647 ,0x61c88647 是一个神奇的数字,让哈希码能均匀的分布在2的N次方的数组里, 即 Entry[] table
- ThreadLocal 往往存放的数据量不会特别大(而且key 是弱引用又会被垃圾回收,及时让数据量更小),这个时候开放地址法简单的结构会显得更省空间,同时数组的查询效率也是非常高,加上第一点的保障,冲突概率也低
参考
- 《Java并发编程的艺术》
- 吃透源码的每一个细节和设计原理–ThreadLocal

