Executor
为了方便并发执行任务,出现了一种专门用来执行任务的实现,也就是Executor。
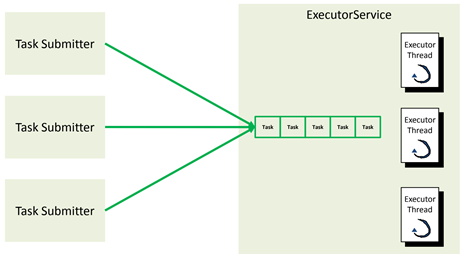
由此,任务提交者不需要再创建管理线程,使用更方便,也减少了开销。Java 里面线程池的顶级接口是 Executor,但是严格意义上讲 Executor 并不是一个线程池,而只是一个执行线程的工具。真正的线程池接口是 ExecutorService。Executor定义规范。
任务与线程执行器的关系
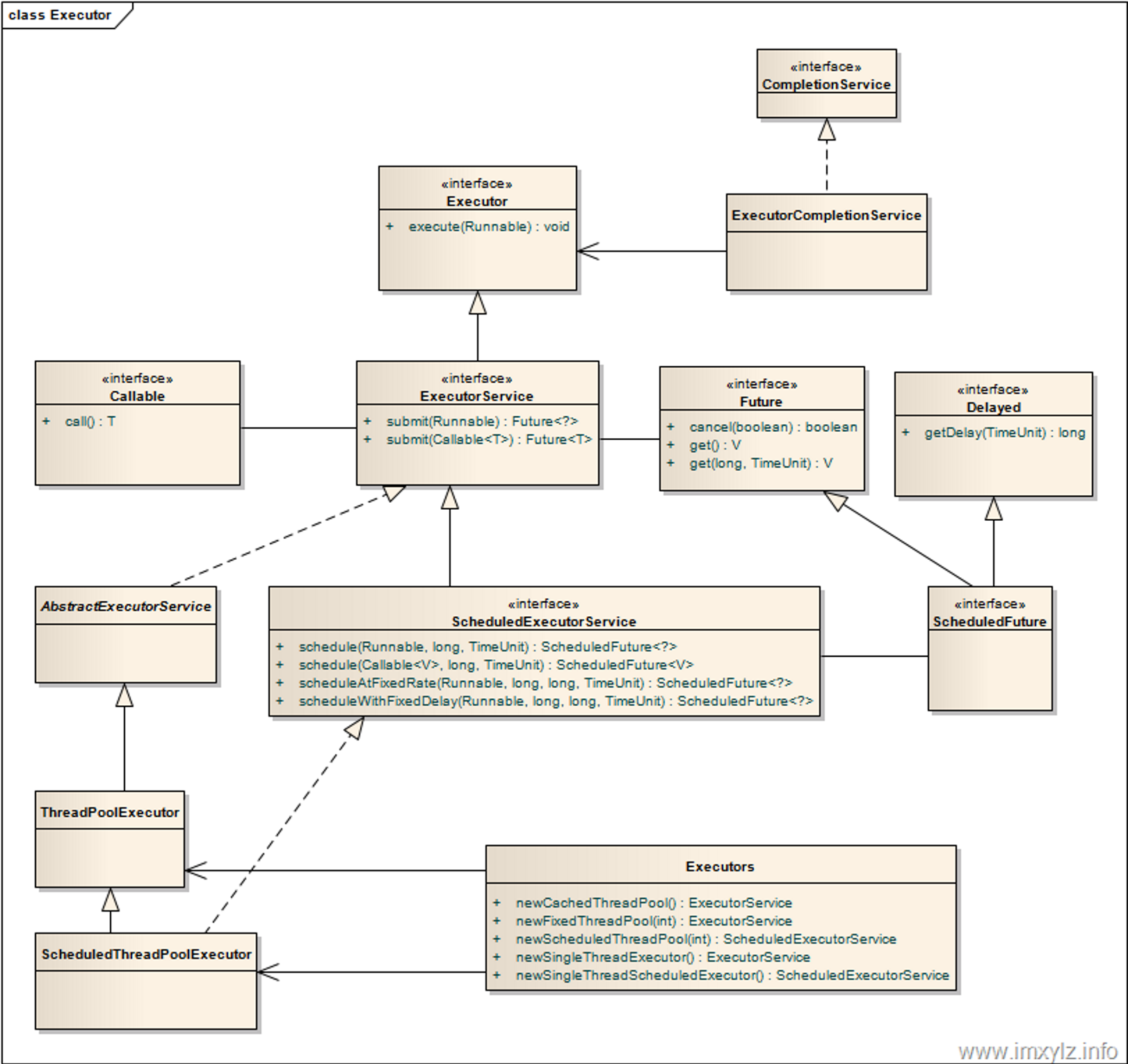
Executor类图
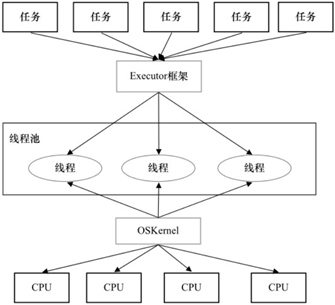
Executor两级调度模型
在上层,Java多线程程序通常把应用分解为若干个任务,然后使用用户级的调度器(Executor框架)将这些任务映射为固定数量的线程;在底层,操作系统内核将这些线程映射到硬件处理器上。
Executor框架结构
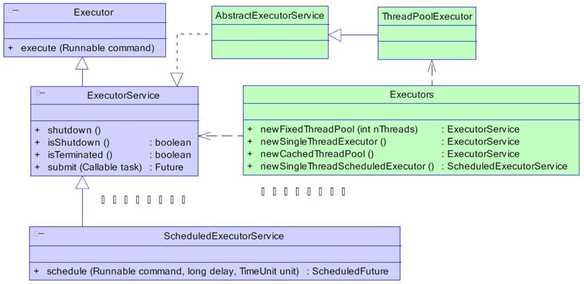
一般的线程池主要分为以下 4 个组成部分:
- 线程池管理器:用于创建并管理线程池
- 工作线程:线程池中的线程
- 任务接口:每个任务必须实现的接口,用于工作线程调度其运行
- 任务队列:用于存放待处理的任务,提供一种缓冲机制
Java 中的线程池是通过 Executor 框架实现的,该框架中用到了 Executor、Executors、ExecutorService、ThreadPoolExecutor 、Callable、Future、FutureTask 这几个类。
Executor结构组件
- 任务。包括被执行任务需要实现的接口:Runnable接口或Callable接口。Runnable接口和Callable接口的实现类,都可以被ThreadPoolExecutor或Scheduled-ThreadPoolExecutor执行
- 任务的执行。包括任务执行机制的核心接口Executor,以及继承自Executor的ExecutorService接口。Executor框架有两个关键类实现了ExecutorService接口(ThreadPoolExecutor和ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor)。
- Executor:Executor框架的基础接口,它将任务的提交与任务的执行分离开来
1 | /** |
- ThreadPoolExecutor:线程池的核心实现类,用来执行被提交的任务
- ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor:线程池实现类,可以在给定的延迟后运行命令,或者定期执行。比Timer更灵活,功能更强大
- 异步计算的结果。包括接口Future和实现Future接口的FutureTask类。
- Future接口和实现Future接口的FutureTask代表异步计算的结果
标记一下比较重要的类:
| ExecutorService: | 真正的线程池接口。 |
|---|---|
| ScheduledExecutorService | 能和Timer/TimerTask类似,解决那些需要任务重复执行的问题。 |
| ThreadPoolExecutor | ExecutorService的默认实现。 |
| ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor | 继承ThreadPoolExecutor的ScheduledExecutorService接口实现,周期性任务调度的类实现。 |
Executors类里面提供了一些静态工厂,生成一些常用的线程池。
- newSingleThreadExecutor:创建一个单线程的线程池。这个线程池只有一个线程在工作,也就是相当于单线程串行执行所有任务。如果这个唯一的线程因为异常结束,那么会有一个新的线程来替代它。此线程池保证所有任务的执行顺序按照任务的提交顺序执行。
- newFixedThreadPool:创建固定大小的线程池。每次提交一个任务就创建一个线程,直到线程达到线程池的最大大小。线程池的大小一旦达到最大值就会保持不变,如果某个线程因为执行异常而结束,那么线程池会补充一个新线程。
- newCachedThreadPool:创建一个可缓存的线程池。如果线程池的大小超过了处理任务所需要的线程,那么就会回收部分空闲(60秒不执行任务)的线程,当任务数增加时,此线程池又可以智能的添加新线程来处理任务。此线程池不会对线程池大小做限制,线程池大小完全依赖于操作系统(或者说JVM)能够创建的最大线程大小。
- newScheduledThreadPool:创建一个大小无限的线程池。此线程池支持定时以及周期性执行任务的需求。
- newSingleThreadExecutor:创建一个单线程的线程池。此线程池支持定时以及周期性执行任务的需求。
ExecutorService
1 | /** |

