概述
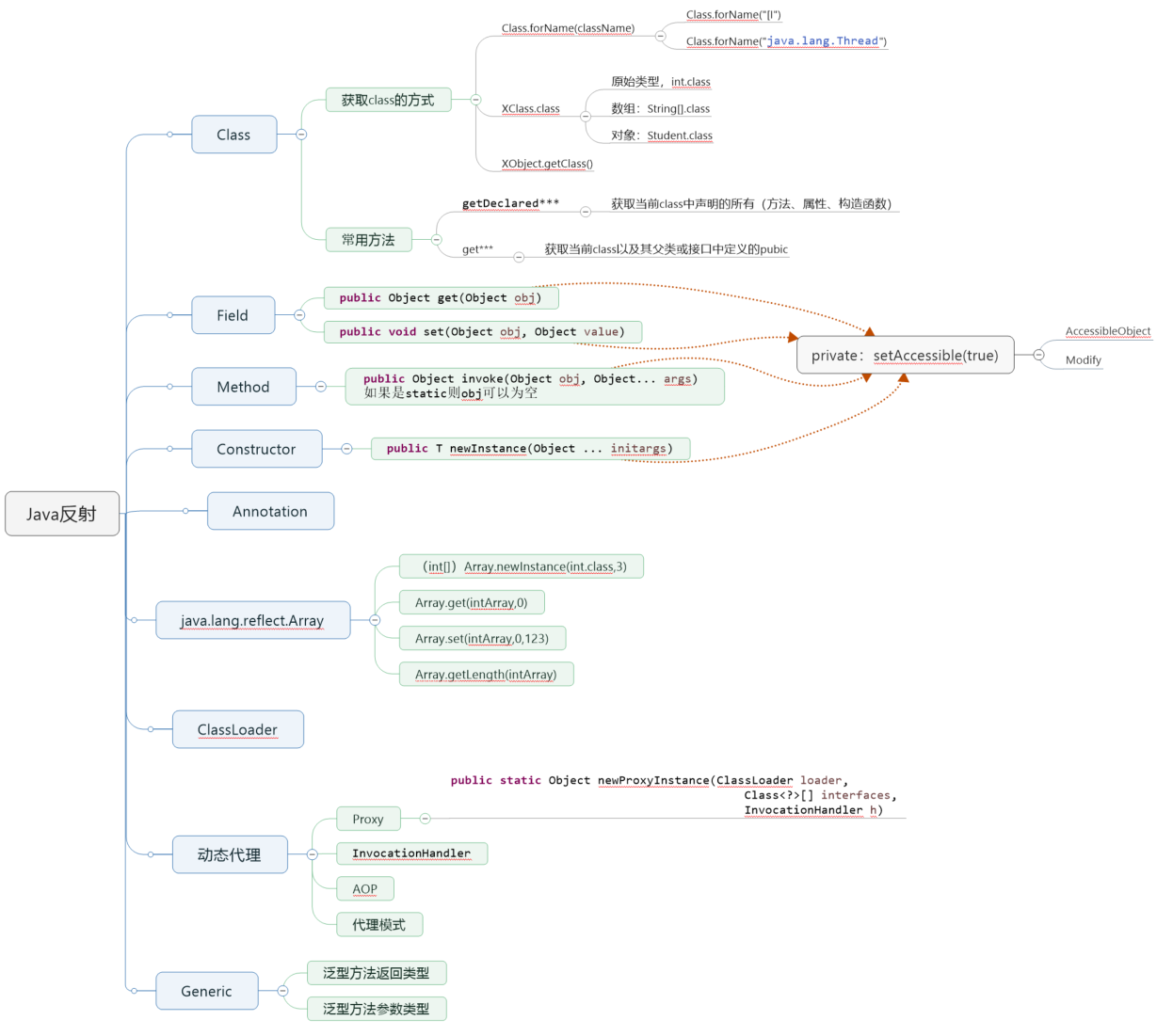
知识点
动态语言
动态语言,是指程序在运行时可以改变其结构:新的函数可以引进,已有的函数可以被删除等结构上的变化。比如常见的 JavaScript 就是动态语言,除此之外 Ruby,Python 等也属于动态语言,而 C、C++则不属于动态语言。从反射角度说 JAVA 属于半动态语言。在Java中如果想获取到运行中对象的结构则需要引入反射的概念。
定义
在 Java 中的反射机制是指在运行状态中,对于任意一个类都能够知道这个类所有的属性和方法;并且对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法;这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能成为 Java 语言的反射机制。
场景
在java中包括两种时期:编译期和运行期,对应的类型就是编译时类型和运行时类型。编译时类型由声明时的对象决定,运行时类型则由实际的对象类型决定(主要表现为行为,对于成员变量则编译时确认)。比如:
1 | //其中编译时类型为 Person,运行时类型为 Man。 |
由于编译时类型无法获取具体方法且程序运行过程中可能会接收外部传入的对象该对象的编译时类型为 Object,但是程序有需要调用该对象的运行时类型的方法。为了解决这些问题,程序需要在运行时发现对象和类的真实信息。然而,如果编译时根本无法预知该对象和类属于哪些类,程序只能依靠运行时信息来发现该对象和类的真实信息,此时就必须使用到反射了。
使用
API
反射API用来生成JVM中的类、接口或则对象的信息。
Class
反射的核心类,可以获取类的属性,方法等信息。class的生成已经加载过程会在JVM章节中进行详细说明。
RTTI(Run-Time Type Identification)运行时类型识别
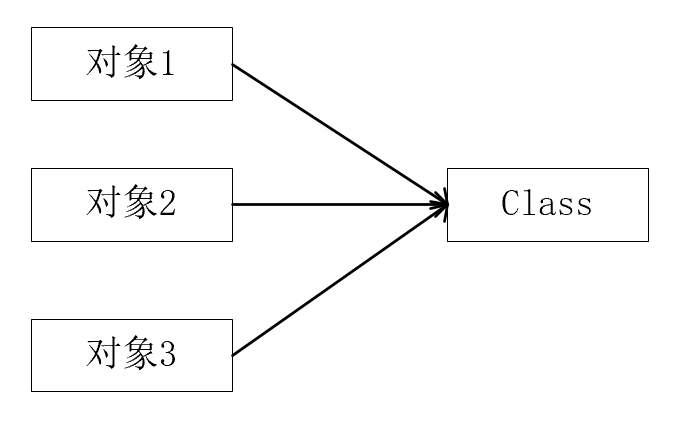
RTTI(Run-Time Type Identification)运行时类型识别,其作用是在运行时识别一个对象的类型和类的信息,这里分两种:传统的”RRTI”,它假定我们在编译期已知道了所有类型(在没有反射机制创建和使用类对象时,一般都是编译期已确定其类型,如new对象时该类必须已定义好),另外一种是反射机制,它允许我们在运行时发现和使用类型的信息。在Java中用来表示运行时类型信息的对应类就是Class类,Class类也是一个实实在在的类,存在于JDK的java.lang包中.
Class的特点
- 在java中万事万物都是对象的概念,使用Class类表示类的对象信息
- 通过关键字class标识的类,在内存中都会有一个与之对应的Class对象,用来描述具体的类型信息
- Class类的构造函数是私有的,因此对应Class对象只能有JVM创建和加载
- Class类的对象作用是运行时提供或获得某个对象的类型信息(反射的来源)
- 类加载器在类被第一次静态调用(比如一个静态方法,一个静态代码块或者new关键字调用构造器,注意contructors其实都是静态的)时会把那个对应的Class对象加载到内存中。
类与对象的关系
Field
Java.lang.reflec 包中的类,表示类的成员变量,可以用来获取和设置类之中的属性值。
class中获取field
| 方法返回值 | 方法名称 | 方法说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Field | getDeclaredField(String name) | 获取指定name名称的(包含private修饰的)字段,不包括继承的字段 |
| Field[] | getDeclaredField() | 获取Class对象所表示的类或接口的所有(包含private修饰的)字段,不包括继承的字段 |
| Field | getField(String name) | 获取指定name名称、具有public修饰的字段,包含继承字段 |
| Field[] | getField() | 获取修饰符为public的字段,包含继承字段 |
field中常用方法
| 方法返回值 | 方法名称 | 方法说明 |
|---|---|---|
| void | set(Object obj, Object value) | 将指定对象变量上此 Field 对象表示的字段设置为指定的新值。 |
| Object | get(Object obj) | 返回指定对象上此 Field 表示的字段的值 |
| Class<?> | getType() | 返回一个 Class 对象,它标识了此Field 对象所表示字段的声明类型。 |
| boolean | isEnumConstant() | 如果此字段表示枚举类型的元素则返回 true;否则返回 false |
| String | toGenericString() | 返回一个描述此 Field(包括其一般类型)的字符串 |
| String | getName() | 返回此 Field 对象表示的字段的名称 |
| Class<?> | getDeclaringClass() | 返回表示类或接口的 Class 对象,该类或接口声明由此 Field 对象表示的字段 |
| void | setAccessible(boolean flag) | 将此对象的 accessible 标志设置为指示的布尔值,即设置其可访问性 |
Method
Java.lang.reflec 包中的类,表示类的方法,它可以用来获取类中的方法信息或者执行方法。
class中的method方法
| 方法返回值 | 方法名称 | 方法说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Method | getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>… parameterTypes) | 返回一个指定参数的Method对象,该对象反映此 Class 对象所表示的类或接口的指定已声明方法。 |
| Method[] | getDeclaredMethod() | 返回 Method 对象的一个数组,这些对象反映此 Class 对象表示的类或接口声明的所有方法,包括公共、保护、默认(包)访问和私有方法,但不包括继承的方法。 |
| Method | getMethod(String name, Class<?>… parameterTypes) | 返回一个 Method 对象,它反映此 Class 对象所表示的类或接口的指定公共成员方法。 |
| Method[] | getMethods() | 返回一个包含某些 Method 对象的数组,这些对象反映此 Class 对象所表示的类或接口(包括那些由该类或接口声明的以及从超类和超接口继承的那些的类或接口)的公共 member 方法。 |
method常用的方法
| 方法返回值 | 方法名称 | 方法说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Object | invoke(Object obj, Object… args) | 对带有指定参数的指定对象调用由此 Method 对象表示的底层方法。 |
| Class<?> | getReturnType() | 返回一个 Class 对象,该对象描述了此 Method 对象所表示的方法的正式返回类型,即方法的返回类型 |
| Type | getGenericReturnType() | 返回表示由此 Method 对象所表示方法的正式返回类型的 Type 对象,也是方法的返回类型。 |
| Class<?>[] | getParameterTypes() | 按照声明顺序返回 Class 对象的数组,这些对象描述了此 Method 对象所表示的方法的形参类型。即返回方法的参数类型组成的数组 |
| Type[] | getGenericParameterTypes() | 按照声明顺序返回 Type 对象的数组,这些对象描述了此 Method 对象所表示的方法的形参类型的,也是返回方法的参数类型 |
| String | getName() | 以 String 形式返回此 Method 对象表示的方法名称,即返回方法的名称 |
| boolean | isVarArgs() | 判断方法是否带可变参数,如果将此方法声明为带有可变数量的参数,则返回 true;否则,返回 false。 |
| String | toGenericString() | 返回描述此 Method 的字符串,包括类型参数。 |
Constructor
Java.lang.reflec 包中的类,表示类的构造方法。
class中获取Constructor
| 方法返回值 | 方法名称 | 方法说明 |
|---|---|---|
| static Class<?> | forName(String className) | 返回与带有给定字符串名的类或接口相关联的 Class 对象。 |
| Constructor |
getConstructor(Class<?>… parameterTypes) | 返回指定参数类型、具有public访问权限的构造函数对象 |
| Constructor<?>[] | getConstructors() | 返回所有具有public访问权限的构造函数的Constructor对象数组 |
| Constructor |
getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>… parameterTypes) | 返回指定参数类型、所有声明的(包括private)构造函数对象 |
| Constructor<?>[] | getDeclaredConstructor() | 返回所有声明的(包括private)构造函数对象 |
| T | newInstance() | 创建此 Class 对象所表示的类的一个新实例。 |
Constructor中的常用方法
| 方法返回值 | 方法名称 | 方法说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Class |
getDeclaringClass() | 返回 Class 对象,该对象表示声明由此 Constructor 对象表示的构造方法的类,其实就是返回真实类型(不包含参数) |
| Type[] | getGenericParameterTypes() | 按照声明顺序返回一组 Type 对象,返回的就是 Constructor对象构造函数的形参类型。 |
| String | getName() | 以字符串形式返回此构造方法的名称。 |
| Class<?>[] | getParameterTypes() | 按照声明顺序返回一组 Class 对象,即返回Constructor 对象所表示构造方法的形参类型 |
| T | newInstance(Object… initargs) | 使用此 Constructor对象表示的构造函数来创建新实例 |
| String | toGenericString() | 返回描述此 Constructor 的字符串,其中包括类型参数。 |
Annotation
参考《JAVA注解》
Array
class中的array
| 方法返回值 | 方法名称 | 方法说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Class<?> | getComponentType() | 返回表示数组元素类型的 Class,即数组的类型 |
| boolean | isArray() | 判定此 Class 对象是否表示一个数组类。 |
array中常用的方法
| 方法返回值 | 方法名称 | 方法说明 |
|---|---|---|
| static Object | set(Object array, int index) | 返回指定数组对象中索引组件的值。 |
| static int | getLength(Object array) | 以 int 形式返回指定数组对象的长度 |
| static object | newInstance(Class<?> componentType, int… dimensions) | 创建一个具有指定类型和维度的新数组。 |
| static Object | newInstance(Class<?> componentType, int length) | 创建一个具有指定的组件类型和长度的新数组。 |
| static void | set(Object array, int index, Object value) | 将指定数组对象中索引组件的值设置为指定的新值。 |
使用步骤:获取Class对象、调用对象方法
获取想要操作的类的 Class 对象,他是反射的核心,通过 Class 对象我们可以任意调用类的方法。可以通过以下方式获取:
- 调用对象的getClass():(new Man()).getClass()
- 调用类的class属性:Man.class
- 使用Class.forName调用类的全路径(最安全,性能最好):Class.forName(“com.sunld.Man”)
调用 Class 类中的方法,既就是反射的使用阶段。
使用反射 API 来操作这些信息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22package com.sunld;
public class ReflectionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取 Man 类的 Class 对象
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.sunld.Man");
// 获取 Man 类的所有方法信息
Method[] method = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m : method) {
System.out.println(m.toString());
}
// 获取 Man 类的所有成员属性信息
Field[] field = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : field) {
System.out.println(f.toString());
}
// 获取 Man 类的所有构造方法信息
Constructor[] constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor c : constructor) {
System.out.println(c.toString());
}
}
}构建对象
Class对象的newInstance()
使用 Class 对象的 newInstance()方法来创建该 Class 对象对应类的实例,但是这种方法要求该 Class 对象对应的类有默认的空构造器。
1 | //获取 Man 类的 Class 对象 |
调用Constructor对象的newInstance()
先使用 Class 对象获取指定的 Constructor 对象,再调用 Constructor 对象的 newInstance() 方法来创建 Class 对象对应类的实例,通过这种方法可以选定构造方法创建实例。
1 | Class<?> clazz=Class.forName("com.sunld.Man"); |
其他
安全性
Java的安全模型
java运行在jvm中,不与外部直接联系,java的安全模型包括:字节码验证器、类加载器、安全管理器、访问控制器等一系列的组件。java通过反射可以处理private方法和属性,说明它绕过了访问控制器。它其实是Java本身为了某种目的而留下的类似于“后门”的东西,它的原理其实是关闭访问安全检查。
Java中访问控制的实现
Field、Method和Constructor类,它们都有一个共同的父类AccessibleObject 。AccessibleObject 有一个公共方法:void setAccessible(boolean flag)。正是这个方法,让我们可以改变动态的打开或者关闭访问安全检查,从而访问到原本是private的方法或域。另外,访问安全检查是一件比较耗时的操作,关闭它反射的性能也会有较大提升。
Java中的作用域(访问控制)
| public | protected | friendly | private | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 在类中 | 可见 | 可见 | 可见 | 可见 |
| 同源文件下的不同类 | 可见 | 可见 | 可见 | 不可见 |
| 同包的不同类 | 可见 | 可见 | 可见 | 不可见 |
| 同包的子类 | 可见 | 可见 | 可见 | 不能继承 |
| 不同包的不同类 | 可见 | 不可见 | 不可见 | 不可见 |
| 不同包的子类 | 可见 | 可见 | 不可见 | 不能继承 |
ClassUtils
在spring的源码中提供了Class反射使用到的常用封装,可以参考修改或者直接使用。
自定义ClassUtils
内省Introspector
一种用于处理javabean的API,提高Java反射的效率
内省Introspector类结构
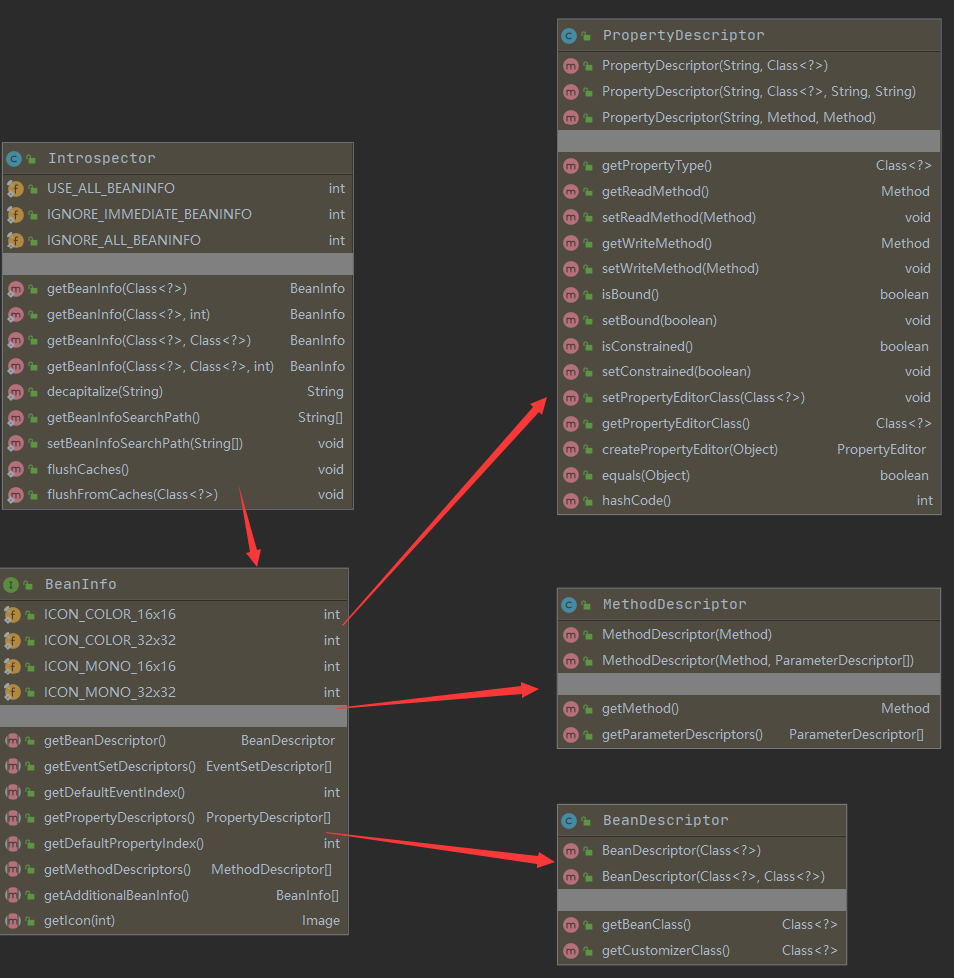
- Introspector:获取JavaBean的BeanInfo
- BeanInfo:通过getPropertyDescriptors 方法和 getMethodDescriptors 方法可以拿到 javaBean 的字段信息列表和 getter 和 setter 方法信息列表
- PropertyDescriptors 可以根据字段直接获得该字段的 getter 和 setter 方法。
- PropertyDescriptor类表示JavaBean类通过存储器导出一个属性。主要方法:
- getPropertyType(),获得属性的Class对象
- getReadMethod(),获得用于读取属性值的方法;getWriteMethod(),获得用于写入属性值的方法;
- hashCode(),获取对象的哈希值;
- setReadMethod(Method readMethod),设置用于读取属性值的方法;
- setWriteMethod(Method writeMethod),设置用于写入属性值的方法。
- MethodDescriptors 可以获得方法的元信息,比如方法名,参数个数,参数字段类型等。
简单示例
1 | package com.sunld; |
org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils
1 | /** |
instanceof和isInstance区别
| 用法 | 功能 | 对象本身 | 父类/接口 | Object | null |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| obj instanceof class | 判断对象是否是某个类型 | true | true | true | false |
| class.isInstance(obj) | 判断对象是否可以转换为这个类 | true | true | true | false |
1 | package com.sunld; |
参考
- 深入理解Java类型信息(Class对象)与反射机制
- 《Java并发编程的艺术》
- 《深入理解Java虚拟机》
- Java中instanceof和isInstance区别详解

